The device and repair of brake system VAZ-2101 Zhiguli
Brake system device
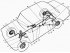
The car has two brake systems: working and parking (pic. 135). The working brake system consists of front and rear wheel brakes and a hydraulic dual-circuit drive to them, powered...
The car has two brake systems: working and parking (pic. 135). The working brake system consists of front and rear wheel brakes and a hydraulic dual-circuit drive to them, powered...
The device and principle of operation of the main brake cylinder
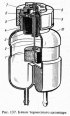
The brake master cylinder is attached to the clutch and brake pedal bracket. Pistons 3 and 4 (pic. 136) activate different circuits. Both pistons take their initial position under...
The brake master cylinder is attached to the clutch and brake pedal bracket. Pistons 3 and 4 (pic. 136) activate different circuits. Both pistons take their initial position under...
Removal, disassembly and inspection of the master brake cylinder
Removal and installation Disconnect the flexible hoses from the master cylinder and close the openings of the hoses and fittings on the cylinder to prevent leakage of fluid from...
Removal and installation Disconnect the flexible hoses from the master cylinder and close the openings of the hoses and fittings on the cylinder to prevent leakage of fluid from...
Hydraulic tank device
The tank is a common reservoir for both hydraulic brake circuits. In order to ensure an independent supply of liquid to each circuit, in the case 10 (pic. 137) the tank is made of...
The tank is a common reservoir for both hydraulic brake circuits. In order to ensure an independent supply of liquid to each circuit, in the case 10 (pic. 137) the tank is made of...
Removal, disassembly and installation of the hydraulic reservoir
Remove the hoses from the tips of the tank and drain the liquid from the tank into the vessel. Plug hose openings to prevent fluid leakage and dirt from entering hoses. Having...
Remove the hoses from the tips of the tank and drain the liquid from the tank into the vessel. Plug hose openings to prevent fluid leakage and dirt from entering hoses. Having...
The device of the pedal assembly of the brakes
Pedals 16 (pic. 138) clutch and 5 brakes are suspended on the bracket 1 by means of an axle made in the form of a bolt. The axis is fixed with a nut 2 in the holes of the cheeks...
Pedals 16 (pic. 138) clutch and 5 brakes are suspended on the bracket 1 by means of an axle made in the form of a bolt. The axis is fixed with a nut 2 in the holes of the cheeks...
Removal and installation of pedal assembly of brakes
To remove the drop assembly, remove the steering shaft bracket, then disconnect the clutch and brake master cylinders from the pedal bracket. Having unscrewed the nuts securing...
To remove the drop assembly, remove the steering shaft bracket, then disconnect the clutch and brake master cylinders from the pedal bracket. Having unscrewed the nuts securing...
Disassembly and assembly of the pedal assembly of the brakes
For disassembly remove the reinforcing spring 12 ( see fig. 138 ), clutch pedals with hook 9, remove the release springs 7 and 14, unscrew the axle nut 15 and, having removed the...
For disassembly remove the reinforcing spring 12 ( see fig. 138 ), clutch pedals with hook 9, remove the release springs 7 and 14, unscrew the axle nut 15 and, having removed the...
Checking and repairing the brake pedal assembly
With a tight movement of the pedals, the working surfaces of the pedals, bushings and axles are inspected. If shallow scratches or traces of oxidation are found on the surfaces of...
With a tight movement of the pedals, the working surfaces of the pedals, bushings and axles are inspected. If shallow scratches or traces of oxidation are found on the surfaces of...
The device and operation of the brake pressure regulator
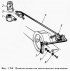
Regulator 3 is connected to the rear brake drive circuit (pic. 139) pressure, which corrects the pressure in the rear brake drive depending on the position of the body relative to...
Regulator 3 is connected to the rear brake drive circuit (pic. 139) pressure, which corrects the pressure in the rear brake drive depending on the position of the body relative to...
Checking the performance of the pressure regulator
To check, install the car on a lift or inspection ditch and clean the pressure regulator and protective cover from dirt. Carefully remove the protective cover from the pressure...
To check, install the car on a lift or inspection ditch and clean the pressure regulator and protective cover from dirt. Carefully remove the protective cover from the pressure...
Removal and installation of the pressure regulator
Disconnect lever 4 ( see fig. 139 ) from the rod 7, and then the bracket 5 from the body and the bracket for fastening the pipelines going to the pressure regulator. The muffler...
Disconnect lever 4 ( see fig. 139 ) from the rod 7, and then the bracket 5 from the body and the bracket for fastening the pipelines going to the pressure regulator. The muffler...
Disassembly, Parts Inspection, and Reassembly of the Pressure Regulator
Removing the plug 6 ( see fig. 140 ), remove the gasket 5, take out the piston 10, the spacer sleeve 3, the seal 7, the spring plate 8, the spring and the thrust washer with the...
Removing the plug 6 ( see fig. 140 ), remove the gasket 5, take out the piston 10, the spacer sleeve 3, the seal 7, the spring plate 8, the spring and the thrust washer with the...
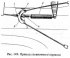
Adjustment of the free travel of the brake pedal, removal of air from the hydraulic drive
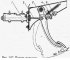
Pedal freeplay 3 (pic. 142) should be 3-5 mm, and full - about 140 mm. The free play is adjusted by moving the brake light switch 5 and then tightening the nut 4. With normal...
Pedal freeplay 3 (pic. 142) should be 3-5 mm, and full - about 140 mm. The free play is adjusted by moving the brake light switch 5 and then tightening the nut 4. With normal...
The device and operation of the front wheel brakes
The brake mechanism of a forward wheel is disk. It consists of the rice. 143 (144) calipers 12 (4) complete with working cylinders, brake disc 18, two brake shoes 16 connecting...
The brake mechanism of a forward wheel is disk. It consists of the rice. 143 (144) calipers 12 (4) complete with working cylinders, brake disc 18, two brake shoes 16 connecting...
Removal and installation of brakes of forward wheels
Before proceeding with the repair of brake mechanisms, they are thoroughly washed with warm water and detergent and dried with a jet of compressed air. The use of gasoline, diesel...
Before proceeding with the repair of brake mechanisms, they are thoroughly washed with warm water and detergent and dried with a jet of compressed air. The use of gasoline, diesel...
Dismantling, checking parts and assembling the front wheel brakes
Disassembly and assembly Disconnect tube 5 ( see fig. 144 ) and remove dust caps 2 from the cylinders. Then, by forcing a jet of compressed air through the brake fluid inlet, the...
Disassembly and assembly Disconnect tube 5 ( see fig. 144 ) and remove dust caps 2 from the cylinders. Then, by forcing a jet of compressed air through the brake fluid inlet, the...
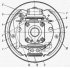
The device and operation of the rear wheel brakes
The brake mechanism of the rear wheel is drum type, with self-aligning pads, which are driven by a wheel hydraulic cylinder 7 (pic. 146). Brake pads 8 with pads 2, wheel cylinder...
The brake mechanism of the rear wheel is drum type, with self-aligning pads, which are driven by a wheel hydraulic cylinder 7 (pic. 146). Brake pads 8 with pads 2, wheel cylinder...
Disassembly, assembly and installation of rear wheel brakes
Disassembly Raise the rear of the car, remove the wheel and, having taken measures to prevent leakage of fluid from the tank, remove the brake drum, for which insert the wheel...
Disassembly Raise the rear of the car, remove the wheel and, having taken measures to prevent leakage of fluid from the tank, remove the brake drum, for which insert the wheel...
Checking the parts of the rear wheel brakes
Piping and connections To prevent failure of the brake system, carefully check the connection of all pipelines. When checking, make sure that: metal pipelines had no cracks, dents...
Piping and connections To prevent failure of the brake system, carefully check the connection of all pipelines. When checking, make sure that: metal pipelines had no cracks, dents...
Adjustment of a backlash between pads and a drum of back brakes
Adjustment order: press the brake pedal with a force of 10-12 kgf to ensure that the pads fit to the drum. Holding the pads in this position, turn the eccentrics 1 and 2 by the...
Adjustment order: press the brake pedal with a force of 10-12 kgf to ensure that the pads fit to the drum. Holding the pads in this position, turn the eccentrics 1 and 2 by the...
The device and operation of the parking brake
The parking brake consists of a mechanical drive and rear wheel brakes. Mechanical drive includes 9 hand lever ( see fig. 135 ), which is connected through the return lever and...
The parking brake consists of a mechanical drive and rear wheel brakes. Mechanical drive includes 9 hand lever ( see fig. 135 ), which is connected through the return lever and...
Parking brake repair
Removal and installation Having set the parking brake lever to the lowest position, disconnect the ends of the cables from the brake shoe drive levers. Loosen locknut 4 ( see fig....
Removal and installation Having set the parking brake lever to the lowest position, disconnect the ends of the cables from the brake shoe drive levers. Loosen locknut 4 ( see fig....
Possible brake problems
Possible malfunctions of the brakes, their cause and remedies are given in Table. 21.
Possible malfunctions of the brakes, their cause and remedies are given in Table. 21.
This section is available on russian, bulgarian, belarusian, ukrainian, serbian, croatian, romanian, polish, slovak, hungarian
More articles from other manuals on VAZ cars:
➠ Chassis: Brake system VAZ-11113 (1996-2003)
➠ Chassis: Brake system VAZ-2105 (1979-2010)
➠ Chassis: Brake system VAZ-21061 (1976-2006)
➠ Chassis: Brake system VAZ-2107 (1982-2012)
➠ Chassis: Brake system VAZ-2108 (1984-2003)
➠ Chassis: Brake system VAZ-2110 (1995-2007)
➠ Chassis: Brake system VAZ-2114 (2004-2013)
➠ Chassis: Brake system VAZ-2121 (1977-1994)
➠ Chassis: Brake system VAZ-11113 (1996-2003)
➠ Chassis: Brake system VAZ-2105 (1979-2010)
➠ Chassis: Brake system VAZ-21061 (1976-2006)
➠ Chassis: Brake system VAZ-2107 (1982-2012)
➠ Chassis: Brake system VAZ-2108 (1984-2003)
➠ Chassis: Brake system VAZ-2110 (1995-2007)
➠ Chassis: Brake system VAZ-2114 (2004-2013)
➠ Chassis: Brake system VAZ-2121 (1977-1994)
Share with friends:
- General information
- Vehicle description
- Vehicle device
- Vehicle operation
- Maintenance
- Main malfunctions
- Applications
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Cooling and lubrication system
- Supply system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Transmission
- Cardan gear
- Rear axle
- Chassis
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Body
- Exterior
- Interior
- Electrical equipment
- Engine electrics
- Equipment and devices
- General information
- Specifications
- Operation and maintenance
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Cooling system
- Lubrication system
- Power and exhaust system
- Ignition system
- Engine electrics
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Car gearbox
- Cardan gear
- Rear axle
- Chassis
- Car suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Body
- Exterior
- Interior
- Doors and locks
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Lighting and signaling
VAZbook.ru © 2017 · Mobile version · Contact with administration · Sitemap: EN BG BY UA RS HR RO PL SK HU · Site search · News and articles
VAZ-1111 · VAZ-11113 · VAZ-2101 · VAZ-21011 · VAZ-2104 · VAZ-2105 · VAZ-21051 · VAZ-2106 · VAZ-21061 · VAZ-2107 · VAZ-21099 · VAZ-2109 · VAZ-2108 · VAZ-2110 · VAZ-2112 · VAZ-2114 · VAZ-2115 · VAZ-2121 · VAZ-21213 · VAZ-21214 ·